Introduction to Psychology
Topic outline
-
Welcome to Introduction to Psychology
Course Introduction
Is Psychology a science? What do our dreams really mean? What causes and treats mental illness? What factors are involved in human behavior? This course aims to answer these questions along with many others. A comprehensive review of the behavior or humans as well as other animals will be provided through each learning module. Topics such as learning, memory, emotions, behavioral disorders, and personality will be explored. The purpose of this course is to provide you with general information in Psychology, which will contribute to your overall body of knowledge.
Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to:- Describe ethical principles that guide psychologists in research and therapy.
- Describe Psychology as a science and identify research methods in Psychology.
- Summarize historical and contemporary theoretical perspectives in Psychology.
- Identify factors in physiological and psychological processes involved in human behavior.
- Describe relations among individuals, groups, and society utilizing discipline-specific terminology.
Adopting institution should provide learners information on how to navigate the course. Consider adding an introductory navigation video. Text description could include, for example:Navigating the Course
This course is set up in Modules covering various topics which may be accessed from the course navigation menu on the left or by scrolling below. Modules may be collapsed in the menu and it the body of the course to minimize scrolling. Each module includes the relevant chapters followed by various activities, which may include discussion forums, listening activities and quizzes, practice quizzes, module tests, and other relevant activities as appropriate for each module. Many items are required and may be marked as completed automatically when the activity has been submitted (the broken check box), but others will marked as done by the student (the solid check box).Please move through the items below and continue through the Learner Support and Getting Started modules before moving on to Module 1. Be sure to check for announcements and due dates to stay on track.
 This course and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network, except where otherwise noted.
This course and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network, except where otherwise noted. -
This module contains all the items you should review and complete before you begin Module 1. Before moving on, be sure to:
- Check the News and Announcements Forum
- Read the Course Syllabus
- Introduce yourself to the class
- Read the instructions for the Q & A Forum
Good luck in the course!-
Use this forum to tell us a little about yourself and your interests. Some topic ideas:
- What is your field of study/research interest or concentration?
- What are you most interested in learning about in this class and why?
- Have you ever taken an online class before?
- Any other information you would like to share with your classmates, such as special interests or activities.
Post a picture! We look forward to meeting you.
-
Use this forum to ask your instructor any questions you have about the course. You may post at any time, and your instructor will respond here. Be as specific as possible.
Please keep in mind that others can see your posts, so do not post any personal information. If you have questions about your grade, please email your instructor directly. You can expect a response to posts and emails within 48 hours M-F, and the next business day on weekends.
- Check the News and Announcements Forum
-
Use the information in this module to customize the template to your needs. This module is currently hidden from students, and available for you to refer to throughout the semester.
-

The Introduction to Psychology portion of this module provides an introduction to the broad field of psychology and the many approaches that psychologists take to understanding human behavior. We will consider how psychologists conduct scientific research, with an overview of some of the most important approaches used and topics studied by psychologists, and also consider the variety of fields in which psychologists work and the careers that are available to people with psychology degrees.
In the Science of Psychology portion of this module you will learn how psychologists develop and test their research ideas; how they measure the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals; and how they analyze and interpret the data they collect. To really understand psychology, you must also understand how and why the research you are reading about was conducted and what the collected data mean. Learning about the principles and practices of psychological research will allow you to critically read, interpret, and evaluate research. (Image Credit Jean-Pol Grandmont Wikimedia licensed CC-BY-SA 4.0)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Understand the etymology of the word “psychology”
- Define psychology
- Understand the merits of an education in psychology
- Understand the importance of Wundt and James in the development of psychology
- Appreciate Freud’s influence on psychology
- Understand the basic tenets of Gestalt psychology
- Appreciate the important role that behaviorism played in psychology’s history
- Understand basic tenets of humanism
- Understand how the cognitive revolution shifted psychology’s focus back to the mind
- Appreciate the diversity of interests and foci within psychology
- Understand basic interests and applications in each of the described areas of psychology
- Demonstrate familiarity with some of the major concepts or important figures in each of the described areas of psychology
- Describe what scientific principles, laws and theories, and research hypotheses are.
- Explain how various scientific research methods can be used to address psychological research questions.
- Discuss general ethical guidelines in conducting psychological research in human and animals.
- Describe the principles of the scientific method and explain its importance in conducting and interpreting research.
- Differentiate laws from theories and explain how research hypotheses are developed and tested.
- Identify the role of the research hypothesis in psychological research.
- Describe the different research methods used by psychologists
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, and archival research
- Compare longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches to research.
- Identify characteristics of an ethical research project using human participant and animals.
- Discuss the procedures that researchers use to ensure that their research with humans and with animals is ethical.
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 1 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 1 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Note the checkboxes to the right that help you track your progress: some are automatic, and some are manual.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module on the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
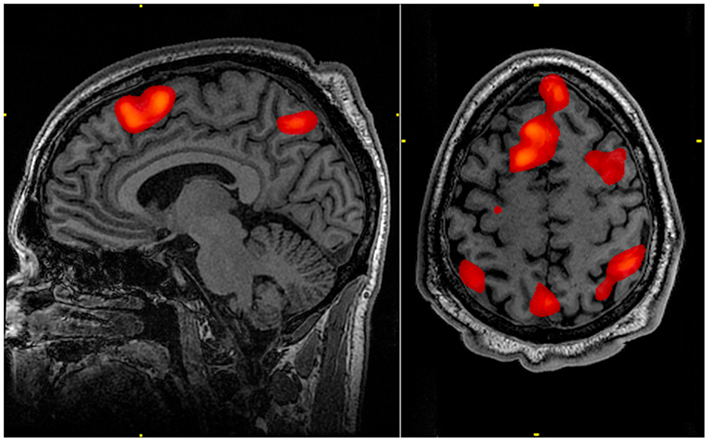
The Physiological Aspects of Psychology segment of this module strives to explain the biological mechanisms that underlie behavior. These physiological and anatomical foundations are the basis for many areas of psychology. In this chapter, you will learn how genetics influence both physiological and psychological traits. You will become familiar with the structure and function of the nervous system. And, finally, you will learn how the nervous system interacts with the endocrine system.
The States of Consciousness segment of this module will discuss states of consciousness with a particular emphasis on sleep. The different stages of sleep will be identified, and sleep disorders will be described. The chapter will close with discussions of altered states of consciousness produced by psychoactive drugs, hypnosis, and meditation. (Image Credit: Public Domain, Wikimedia)Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Discuss how gene-environment interactions are critical for the expression of physical and psychological characteristics
- Identify the basic parts of a neuron
- Describe how neurons communicate with each other
- Describe the difference between the central and peripheral nervous systems
- Define the concepts of brain plasticity, neurogenesis, and brain lateralization.
- Identify the major glands of the endocrine system
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 2 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 2 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-

This module will provide an overview of how sensory information is received and processed by the nervous system and how that affects our conscious experience of the world. We begin by learning the distinction between sensation and perception. Then we consider the physical properties of light and sound stimuli, along with an overview of the basic structure and function of the major sensory systems. A discussion of a historically important theory of perception called Gestalt is included.
We will explore the fascinating tale of how you have grown and developed into the person you are today. We also look at some ideas about who you will grow into tomorrow. Yours is a story of lifespan development, from the start of life to the end. (Image Credit: Cory Zanker)Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Distinguish between sensation and perception
- Describe the concepts of absolute threshold and difference threshold
- Discuss the roles attention, motivation, and sensory adaptation play in perception
- Describe the basic anatomy of the visual system
- Discuss how rods and cones contribute to different aspects of vision
- Describe how monocular and binocular cues are used in the perception of depth
- Describe the basic anatomy and function of the auditory system
- Explain how we encode and perceive pitch
- Discuss how we localize sound
- Describe the basic functions of the chemical senses
- Explain the basic functions of the somatosensory, nociceptive, and thermoceptive sensory systems
- Describe the basic functions of the vestibular, proprioceptive, and kinesthetic sensory systems
- Define and distinguish between the three domains of development: physical, cognitive and psychosocial
- Discuss the normative approach to development
- Understand the three major issues in development: continuity and discontinuity, one common course of development or many unique courses of development, and nature versus nurture
- Discuss Freud’s theory of psychosexual development
- Describe the major tasks of child and adult psychosocial development according to Erikson
- Discuss Piaget’s view of cognitive development and apply the stages to understanding childhood cognition
- Describe Kohlberg’s theory of moral development
- Describe the stages of prenatal development and recognize the importance of prenatal care
- Discuss physical, cognitive, and emotional development that occurs from infancy through childhood
- Discuss physical, cognitive, and emotional development that occurs during adolescence
- Discuss physical, cognitive, and emotional development that occurs in adulthood
- Discuss hospice care
- Describe the five stages of grief
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 3 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 3 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-

The Learning segment of this module focuses on the primary ways in which learning occurs.
In the Thinking and Intelligence segment of this module, we will focus on high-level cognitive processes. As a part of this discussion, we will consider thinking and briefly explore the development and use of language. We will also discuss problem solving and creativity before ending with a discussion of how intelligence is measured and how our biology and environments interact to affect intelligence. After finishing this chapter, you will have a greater appreciation of the higher-level cognitive processes that contribute to our distinctiveness as a species. (Image Credit Drflet Wikimedia licensed CC-BY-SA 3.0)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:1) Define the term intelligence2) Describe the purposes and benefits of intelligence testing3) Define language and demonstrate familiarity with the components of language4) Describe cognition5) Describe how genetics and environment affect intelligence6) Describe the difference between a learning disability and a developmental disorderTo achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 4 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 4 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
- Read the Module 4 Introduction
-

We have an amazing capacity for memory, but how, exactly, do we process and store information? Are there different kinds of memory, and if so, what characterizes the different types? How, exactly, do we retrieve our memories? And why do we forget? The Memory segment of this module will explore these questions as we learn about memory.
In the Emotion and Motivation segment of this module, we will explore issues relating to both motivation and emotion. We will begin with a discussion of several theories that have been proposed to explain motivation and why we engage in a given behavior. You will learn about the physiological needs that drive some human behaviors, as well as the importance of our social experiences in influencing our actions. This segment will close with a discussion of emotion. You will learn about several theories that have been proposed to explain how emotion occurs, the biological underpinnings of emotion, and the universality of emotions. (Credit: Modification of work by Cory Zanker)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Discuss the three basic functions of memory
- Describe the three stages of memory storage
- Describe and distinguish between procedural and declarative memory and semantic and episodic memory
- Explain the brain functions involved in memory
- Recognize the roles of the hippocampus, amygdala, and cerebellum
- Compare and contrast the two types of amnesia
- Discuss the unreliability of eyewitness testimony
- Discuss encoding failure
- Discuss the various memory errors
- Compare and contrast the two types of interference
- Recognize and apply memory-enhancing strategies
- Recognize and apply effective study techniques
- Define intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
- Understand that instincts, drive reduction, self-efficacy, and social motives have all been proposed as theories of motivation
- Explain the basic concepts associated with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
- Describe how hunger and eating are regulated
- Differentiate between levels of overweight and obesity and the associated health consequences
- Explain the health consequences resulting from anorexia and bulimia nervosa
- Understand basic biological mechanisms regulating sexual behavior and motivation
- Appreciate the importance of Alfred Kinsey’s research on human sexuality
- Recognize the contributions that William Masters and Virginia Johnson’s research made to our understanding of the sexual response cycle
- Define sexual orientation and gender identity
- Explain the major theories of emotion
- Describe the role that limbic structures play in emotional processing
- Understand the ubiquitous nature of producing and recognizing emotional expression
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 5 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 5 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-

In the Personality segment of this module, we will consider the wide variety of personality traits found in human beings. We’ll consider how and when personality influences our behavior, and how well we perceive the personalities of others. We will also consider how psychologists measure personality, and the extent to which personality is caused by nature versus nurture. The fundamental goal of personality psychologists is to understand what makes people different from each other (the study of individual differences), but they also find that people who share genes (as do Paula Bernstein and Elyse Schein) have a remarkable similarity in personality.
The Social Psychology segment of this module explores how the presence of other people influences the behavior of individuals, dyads, and groups. Social factors can determine whether human behavior tends toward conflict or harmony. (Image Credit: Modification of work by Nicolas Alejandro)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Define personality
- Describe early theories about personality development
- Describe the strengths and limitations of the psychodynamic approach to explaining personality.
- Summarize the accomplishments of the neo-Freudians.
- Identify the major contributions of the humanistic approach to understanding personality.
- Describe the behaviorist, cognitive, and social cognitive perspective on personality.
- Describe the trait approach to understanding personality and the influences of personality on behaviors.
- Discuss how situations play a role in one’s personality.
- Describe what MMPI is and how people use MMPI to measure personalities.
- Describe various projective tests.
- Discuss how personality may differ across cultures.
- Discuss ways to study personalities across cultures.
- Define social psychology
- Describe situational versus dispositional influences on behavior
- Describe the fundamental attribution error
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
- Define attitude
- Describe how people’s attitudes are internally changed through cognitive dissonance
- Explain how people’s attitudes are externally changed through persuasion
- Describe the peripheral and central routes to persuasion
- Explain the Asch effect
- Define conformity and types of social influence
- Describe Stanley Milgram’s experiment and its implications
- Define groupthink, social facilitation, and social loafing
- Define and distinguish among prejudice, stereotypes, and discrimination
- Provide examples of prejudice, stereotypes, and discrimination
- Explain why prejudice and discrimination exist
- Define aggression
- Define cyberbullying
- Describe the bystander effect
- Describe altruism
- Describe conditions that influence the formation of relationships
- Identify what attracts people to each other
- Describe the triangular theory of love
- Explain social exchange theory in relationships
- Review the principles of social cognition, including the fundamentals of how we form judgments about other people.
- Define the concept of attitude and review the ways that attitudes are developed and changed, and how attitudes relate to behavior.
- Summarize the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to human altruism.
- Provide an overview of the causes of human aggression.
- Explain the situations under which people conform to others and their motivations for doing so.
- Summarize the advantages and disadvantages of working together in groups to perform tasks and make decisions.
- Review the factors that can increase group productivity.
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 6 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 6 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-

The goal of the Treatment of Psychological Disorders segment of this module is to review the techniques that are used to treat psychological disorders. Just as psychologists consider the causes of disorder in terms of the bio-psycho-social model of illness, treatment is also based on psychological, biological, and social approaches.
- The psychological approach to reducing disorder involves providing help to individuals or families through psychological therapy, including psychoanalysis, humanistic-oriented therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and other approaches.
- The biomedical approach to reducing disorders is based on the use of medications to treat mental disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety, and the employment of brain intervention techniques, including electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), and psychosurgery.
- The social approach to reducing disorder focuses on changing the social environment in which individuals live to reduce the underlying causes of the disorder. These approaches include group, couples, and family therapy, as well as community outreach programs. The community approach is likely to be the most effective of the three approaches because it focuses not only on treatment but also on the prevention of disorders (World Health Organization, 2004)1. (Image Credit tronvillain Wikimedia licensed CC-BY-SA 4.0)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
1) Outline and differentiate the psychodynamic, humanistic, behavioral, and cognitive approaches to psychotherapy.
2) Classify the different types of drugs used in the treatment of mental disorders and explain how they each work to reduce disorder.
3) Critically evaluate direct brain intervention methods that may be used by doctors to treat patients who do not respond to drugs or other therapy.
4) Explain the advantages of group therapy and self-help groups for treating disorders.
5) Recognize the goal of substance-related and addictive disorders treatment
6). Summarize the ways that scientists evaluate the effectiveness of psychological, behavioral, and community service approaches to preventing and reducing disorders.
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 7 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 7 Pressbooks book
- Complete all activities in the module
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
