World Regional Geography
Topic outline
-
Welcome to World Regional Geography
Course Introduction
This course will explore world regional geography via the concept of globalization as it is experienced from a world regional perspective. We will discuss different areas of the world and the social, cultural, environmental and other aspects that shape them and their interaction with the rest of the world.Upon completion of this course, you will be able to:-
Name important physical and cultural locations across the globe, and locate them on maps.
-
Identify principles and standard practices of mapping, and modern techniques for computer map analysis and remote sensing.
-
Explain important factors that have shaped the physical features of the planet, and their mechanisms
-
Recognize important factors that have shaped the human features of the planet (political, cultural, historical, economic, etc.), and their mechanisms.
-
Summarize how the global environment impacts, and is impacted, by humans.
-
Interpret geographically-related topics appearing in modern media.
Structure of the Course
This course is structured by weekly Modules and corresponding chapter topics. Each chapter covers a specific region with relevant countries within that region for exploration and discussion. Each week you will be assigned a chapter reading, assignment, quiz or exam and three discussion board posts based on a specific chapter topic.
Navigating the Course
This course is set up in Modules covering various topics which may be accessed from the course navigation menu on the left or by scrolling below. Modules may be collapsed in the menu and it the body of the course to minimize scrolling. Each module includes the relevant chapters followed by various activities, which may include discussion forums, listening activities and quizzes, practice quizzes, module tests, and other relevant activities as appropriate for each module. Many items are required and may be marked as completed automatically when the activity has been submitted (the broken check box), but others will marked as done by the student (the solid check box).
Please move through the items below and continue through the Learner Support and Getting Started modules before moving on to Module 1. Be sure to check for announcements and due dates to stay on track.
 This course and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License by Jessica Hawkes, Tyler Johnson, Rusti Liner, Mathab A. Lodhi, Neusa McWilliams, Jeffrey Stepp, and Peter Yaukey, and by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network, except where otherwise noted.
This course and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License by Jessica Hawkes, Tyler Johnson, Rusti Liner, Mathab A. Lodhi, Neusa McWilliams, Jeffrey Stepp, and Peter Yaukey, and by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network, except where otherwise noted. -
-
This module contains all the items you should review and complete before you begin Module 1. Before moving on, be sure to:
- Check the News and Announcements Forum
- Read the Course Syllabus
- Introduce yourself to the class
- Read the instructions for the Q & A Forum
Good luck in the course!-
Use this forum to tell us a little about yourself and your interests. Some topic ideas:
- What is your field of study/research interest or concentration?
- What are you most interested in learning about in this class and why?
- Have you ever taken an online class before?
- Any other information you would like to share with your classmates, such as special interests or activities.
Post a picture! We look forward to meeting you.
-
Use this forum to ask your instructor any questions you have about the course. You may post at any time, and your instructor will respond here. Be as specific as possible.
Please keep in mind that others can see your posts, so do not post any personal information. If you have questions about your grade, please email your instructor directly. You can expect a response to posts and emails within [X] hours. [Recommendation is 24 hours M-F, next business day on weekends.]
Subscription should be set to Auto.
*Red Text Left to indicate where adopting instructor should enter information*
- Check the News and Announcements Forum
-
Use the information in this module to customize the template to your needs. This module is currently hidden from students, and available for you to refer to throughout the semester.
-

Problemsmith, CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
The discipline of geography bridges the social sciences with the physical sciences and can provide a framework for understanding our world. By studying geography, we can begin to understand the relationships and common factors that tie our human community together. The world is undergoing globalization on a massive scale as a result of the rapid transfer of information and technology and the growth of modes of transportation and communication. The more we understand our world, the better prepared we will be to address the issues that confront our future.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:1. Identify the focus of geography and the two main branches of the discipline. (CLO 3 & 4)2. Recognize the tools geographers use to study the earth’s surface. (CLO 2)3. Summarize the grid system of latitude and longitude and how it relates to seasons and time zones. (CLO 2)4. Distinguish between the different types of regional distinctions recognized in geography. (CLO 1)5. Discuss the spatial nature of geography and how each place or region is examined, analyzed, andcompared with other places or regions. (CLO 2)6. Determine the basic geographic realms and their location. (CLO 1)To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 1 Introduction
- Read Chapter #1 - Introduction to the World in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 1 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course learning outcomes 3 & 4, and module learning objective 1. Then, you must respond to 2 of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are required to post three times a week, every week.
All posts are due on Mondays by midnight.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
What is the main focus of Geography and the two main branches of the discipline?
- Read the Module 1 Introduction
-

"A London Street" by Peter Yaukey is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
Europe is a region for which many Louisianans have direct ancestral ties, and many American cultural features can be traced back to European origins. Today it has achieved advanced industrial development and enjoys a relatively high level of affluence and international influence. It contains dozens of nations with distinct characteristics and histories, providing a rich cultural variety in a relatively small land area.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Name and know the locations of the nations of Europe, and their major cities (CLO 1, 4).
- Describe the various climate types and land forms of the European continent (CLO 1, 3, 5).
- Outline how the Roman Empire and the Viking era contributed to European development (CLO 1, 4).
- Explain the major developments that prompted the Industrial Revolution, and describe the distribution of industrialization in Europe today (CLO 1, 4, 6).
- Identify the three main language groups and the three main religious denominations of Europe (CLO 1, 4, 6).
- Explain how Eastern Europe and Western Europe were divided by communism and how they united again (CLO 1, 4).
- Describe the various aspects of transition from socialism systems to capitalist democracies (CLO 4, 6).
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 3 Introduction
- Read Chapter #2: Europe in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 2 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course outcomes 1, 3, 4 and 6, and module learning objectives 1 and 2. Then, you must respond to TWO of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are not required to post more than once, but feel free to respond to other posts and engage with your classmates
All three posts are due on Mondays by midnight, CST.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
How would traveling (as a tourist) from nation to nation in Europe, be a different experience than traveling from state to state in the United States?
- Name and know the locations of the nations of Europe, and their major cities (CLO 1, 4).
-
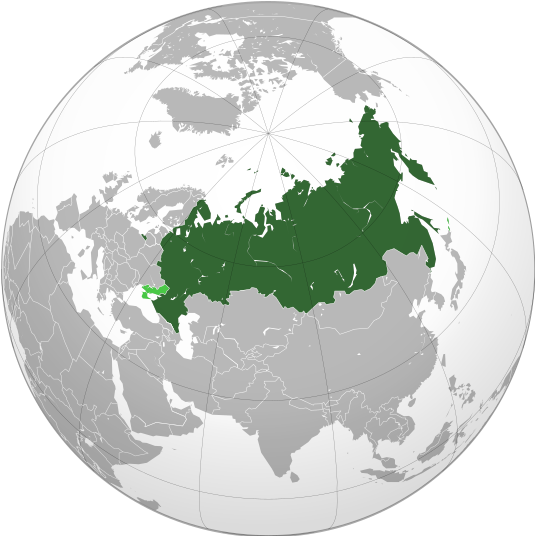
UnixBased, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
I have 100,000 rivers, 12 active volcanoes, the longest railway and I am the largest country in the world! Who am I?
R U S S I A

Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Identify Russia’s climatic influences and physical regions. (CLO 1 & 3)
- Determine how the czars expanded their territorial power to create the Russian Empire. (CLO 4)
- Describe some of the environmental problems facing the Russian republics today. (CLO 5)
- Define the main tenets of a socialist economy. (CLO 4)
- Explain why the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) collapsed. (CLO 4)
- Describe the post-Soviet economic and political situation. (CLO 4)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 3 Introduction
- Read Chapter #3 -Russia in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization
- Complete the Module 3 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.-
-
This assignment assesses course outcome (CLO 5), and module learning objective 3.
Write a 350-word essay in response to the following prompt. The essay must be submitted as a Microsoft Word (docx) file and must have 1-inch margins, use double spacing throughout with 12pt font. Proper grammar and spelling will be graded.
Describe some of the environmental problems facing the Russian republics today. -
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course outcome (CLO 4), and module learning objective 4. Then, you must respond to TWO of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are not required to post more than once, but feel free to respond to other posts and engage with your classmates
All three posts are due on Mondays by midnight, CST.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
Define the main tenets of a socialist economy.
-

Glacier National Park, by Dave Sizer licensed CC-BY 2.0
The realm of North America as a continent extends from the polar regions of the Arctic in northern Canada and Alaska all the way south through Mexico and the countries of Central America. Geographers usually study the continent by dividing it into two separate realms based on differences in physical and cultural geography. The United States and Canada share similar physical geography characteristics as well as a common development history with either a British or French colonial legacy. Mexico and Central America are dominated by more tropical climates and were colonized mainly by the Spanish. The United States and Canada—the second- and third-largest countries in the world in physical area, respectively—make up more than 13 percent of the world’s total landmass. The Atlantic Ocean borders their eastern edge, and the Pacific Ocean creates their western boundary. To the north is the Arctic Ocean. The North American region is highly urbanized—about 80 percent of the population lives in cities—but other vast areas, especially in Canada, are sparsely populated. Although some natives remain, most of North America’s diverse population consists of immigrants or descendants of immigrants from other world regions. The United States is the world’s largest economy, and both countries enjoy high standards of living as technologically developed countries.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Define the physiographic regions of North America. (CLO 1 & 3)
- Explain the two dominant climate patterns in North America. (CLO 3 & 5)
- Find out which three European countries had the most significant early influence on North America, what parts of the region they dominated, and what their long-term impacts have been. (CLO 4 & 5)
- Determine the population distribution of the United States and Canada. (CLO 2, 4, & 5)
- Explain which economic patterns helped the United States become the world’s largest economy, Canada's key economic sectors, and the connections between the U.S. and Canadian economies. (CLO 4 & 5)
- Explain the concepts of the cultural melting pot and the American Dream and how they have contributed to American society and culture and been exported globally. (CLO 4 & 6)
- Explain how physical geography has contributed to economic activities. (CLO 3, 4, & 5)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 4 Introduction
- Read Chapter #4 -North America in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization
- Complete the Module 4 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
*-
-
Instructions
This assignment addresses course outcomes 4 & 5 and module learning objective 3.
Write a 250-word essay in response to the following prompt. The essay must be submitted as a Microsoft Word (docx) file and must have 1-inch margins, use double spacing throughout its length, and use Times New Roman font.
Choose one of the three European countries that had the most significant impact on North America and describe which region or regions it affected the most, providing two specific examples of long-term effects on the region(s).
- Define the physiographic regions of North America. (CLO 1 & 3)
-

"Garifuna SanIsidro 1996" by Eve Demaziere is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
Middle America, the geographic realm between the United States and the continent of South America, consists of three main regions: the Caribbean, Mexico, and the Central American republics.
The Caribbean region, the most culturally diverse of the three, consists of more than seven thousand islands that stretch from the Bahamas to Barbados. The four largest islands of the Caribbean make up the Greater Antilles, which include Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico. Hispaniola is split between Haiti in the west and the Dominican Republic in the east. The smaller islands, extending all the way to South America, make up the Lesser Antilles. The island that is farthest south is Trinidad, just off the coast of Venezuela. The Bahamas, the closest islands to the US mainland, are located in the Atlantic Ocean but are associated with the Caribbean region. The Caribbean region is surrounded by bodies of saltwater: the Caribbean Sea in the center, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the North Atlantic to the east.
Central America refers to the seven states south of Mexico: Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. Panama borders the South American country of Colombia. During the colonial era, from 1492 to 1821, Panama was included in the part of South America controlled by the Spanish (it was considered part of the Viceroyalty of Peru). The Pacific Ocean borders Central America to the west, and the Caribbean Sea borders these countries to the east. While most of the republics have both a Caribbean and a Pacific coastline, Belize has only a Caribbean coast, and El Salvador has only a Pacific coast.
Garifuna San Isidro 1996-05, Eve Demaziare, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Garifuna_SanIsidro_1996-05_2.jpg, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 Generic, 2.0 Generic and 1.0 Generic license.Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Define the differences between the rimland and the mainland. (CO 1 & 4)
- Summarize the impact of European colonialism on Middle America. (CO 3, 4 & 5)
- Distinguish between the Mayan and Aztec Empires and identify which the Spanish defeated. (CO 1 & 4)
- Outline the socioeconomic classes in Mexico and explain the ethnic differences of each. (CLO 4)
- Describe how the physical environment has affected human activity in Central America and how the various republics differ from each other. (CLO 3, 4, 5, & 6)
- Outline the various ways in which the United States has affected the Caribbean and Central America, including the creation of NAFTA and the drug trade. (CLO 4, 5, & 6)
- Explain how tourism has become the main means of economic development for most of the Caribbean. (CLO 4, 5, & 6)
- Describe how and why hurricanes form and why they can be so dangerous. (CLO 3, 4, 5, & 6)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 5 Introduction.
- Read Chapter #5 - Introduction to the World in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization
- Complete the Module 5 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item. - Define the differences between the rimland and the mainland. (CO 1 & 4)
-
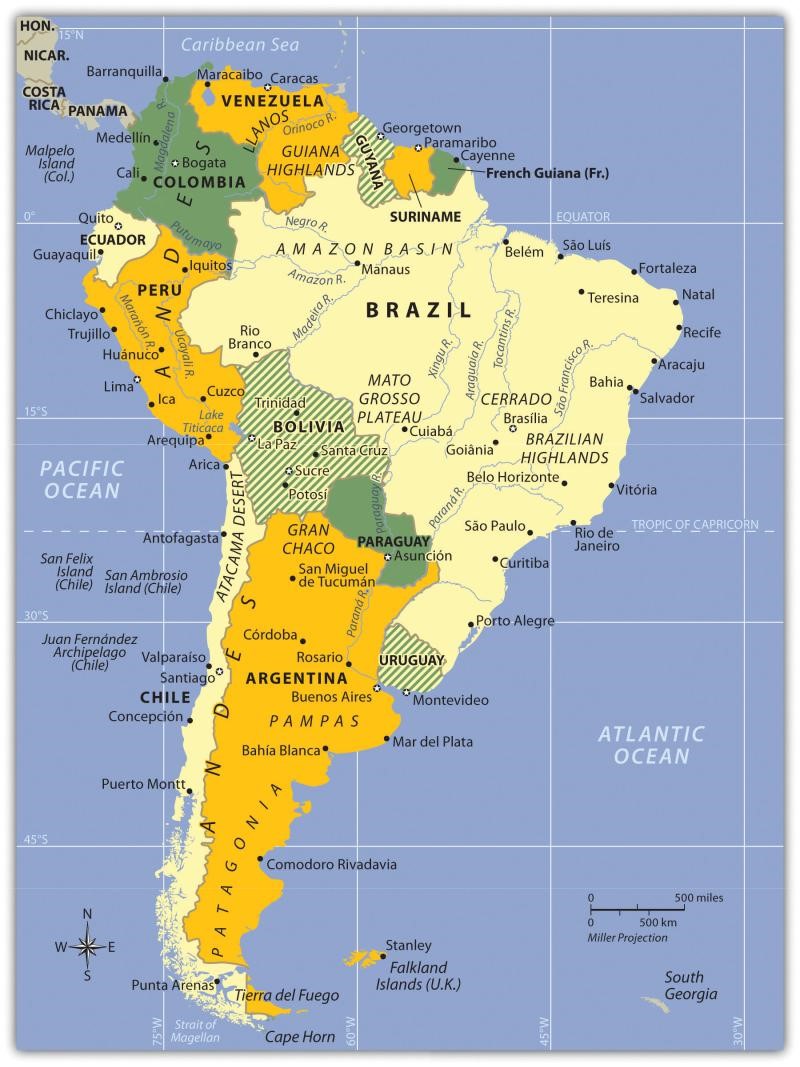 High source, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
High source, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia CommonsEuropeans called the Western Hemisphere the New World. South America is the realm consisting of the southern portion of the New World. This realm includes the entire continent of South America, which is smaller in physical area than North America.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Summarize the main physical features and characteristics of South America.
- Explain how European colonialism dominated the realm and divided up the continent.
- Outline the main cultural realms of South America. Describe each realm’s main ethnic majority and explain how colonialism impacted each region.
- Summarize how the South American countries are attempting to integrate their economies.
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 6 Introduction
- Read Chapter 6: South America in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 6 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities.
-
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course learning outcomes 3 & 5, and module learning objectives 2 & 4. Then, you must respond to 2 of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are required to post three times a week, every week.
All posts are due on Mondays by midnight.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
How does the core-periphery spatial relationship apply to Uruguay, Argentina, and Chile?
- Summarize the main physical features and characteristics of South America.
-
https://images.app.goo.gl/P2peknoAwU24DDAM6
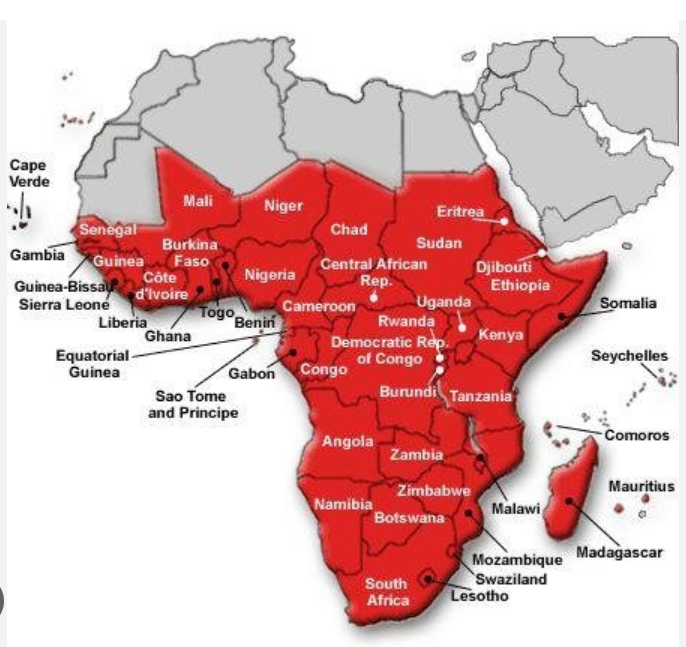
Subsaharan Africa includes the African countries south of the Sahara Desert. The African Transition Zone cuts across the southern edge of the Sahara Desert at the widest portion of the continent. Many of the countries in the African Transition Zone are included in the realm of Subsaharan Africa. The realm can be further broken down into regional components: Central Africa, East Africa, West Africa, and Southern Africa. At the eastern end of the African Transition Zone is the Horn of Africa, which is often included in the region of East Africa.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Summarize the basic geography of Subsaharan Africa. Identify the African Transition Zone, including the transitions that are occurring in the zone. Locate the main features on a map.
- Understand how early kingdoms flourished in Subsaharan Africa before the colonial era. Identify how selective groups in these kingdoms participated in the supply operations for the slave trade.
- Explain the effects of colonialism. Outline how countries have transitioned from colonies to independent nations, including the many issues involved in this transition.
- Explain how family size and economic activities are related to population growth.
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 7 Introduction
- Read Chapter 7 in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization[Include all reading assignments here that are outside of Moodle. Be as
concise as possible. More information can be included in the
third-party section below, if necessary.]
- Complete the Module 7 assignment, discussion board posts (3), Module 7 Quiz, and h5p activities.
-
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course learning outcomes 3 & 5, and module learning objectives 1 & 2. Then, you must respond to 2 of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are required to post three times a week, every week.
All posts are due on Mondays by midnight.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
How did the Cold War influence Southern African countries?
- Summarize the basic geography of Subsaharan Africa. Identify the African Transition Zone, including the transitions that are occurring in the zone. Locate the main features on a map.
-
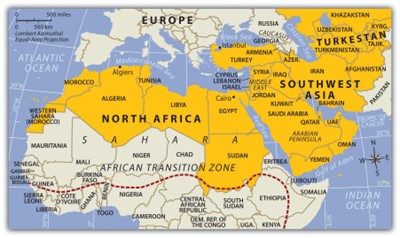
The countries of the realm share three key dominant traits that influence all other human activities:1) is the dry or arid type B climate that dominates and covers most of the physical area of this realm; 2) is Islam: most of the people in the realm are Muslims. Islam acts as more than just a religion. It also serves as a strong cultural force that has historically unified or divided people of this realm. The divisive nature of the religion has often resulted in serious political confrontations within the realm between groups of different Islamic ideologies; and 3) is the availability of significant natural resources. North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Turkestan all have significant reserves of oil, natural gas, and important minerals. It stands to reason that not every country has the same reserves and that some of the countries have very few or none at all. However, in terms of how the countries gain national wealth, it is the export of oil that has dominated the economic activity as it relates to the global community.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Describe three basic traits the countries of the realm shares in common.
- Outline the two cultural hearths of this realm and explain why they developed where they did.
- Describe the early life of Muhammad and the origins of Islam.
- Analyze the differences and similarities among the three main monotheistic religions.
- Outline the unique geographic qualities of the Maghreb and explain how this region is connected to Europe.
- Describe the main qualities of the African Transition Zone and explain how the dynamics of this zone are affecting the country of Sudan.
- Describe the types of governments found in the region.
- Explain why Turkey wants to be a member of the European Union (EU) and why it has not been accepted.
- Summarize how Central Asia has been transitioning from a Soviet-dominated region to independent states and what has been occurring in the various states to adapt to the new economic environment.
- Explain the geopolitical history of Afghanistan and why this area has been so difficult to govern under a central government.
To achieve the above listed objectives:
- Read the Module 8 Introduction
- Read and view the materials in the Module 8
- Read Chapter 8 on North Africa and Southwest Asia in [Chapter 8: North Africa and Southwest Asia – World Regional Geography (pressbooks.pub)]
- Complete all Module 8 activities.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
Chapter 8: North Africa and Southwest Asia – World Regional Geography (pressbooks.pub)
- Describe three basic traits the countries of the realm shares in common.
-
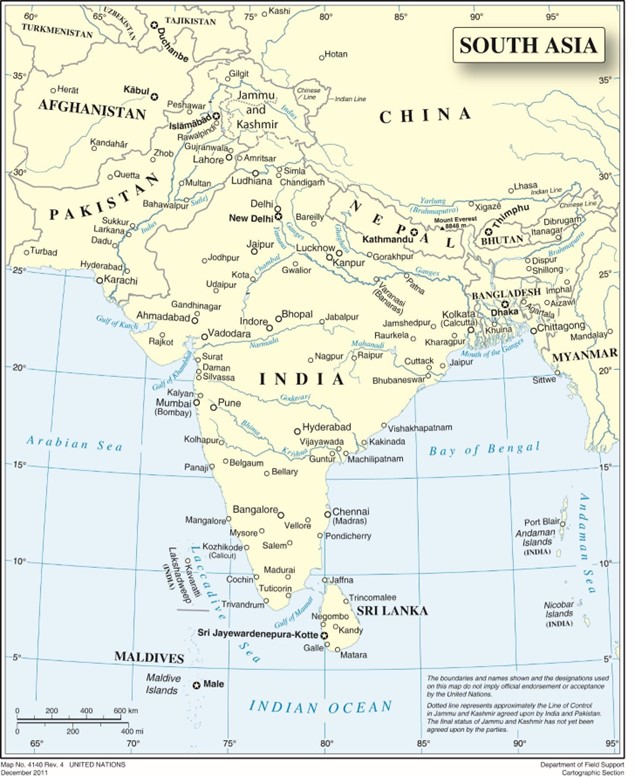
UN, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The South Asian realm shaped by centuries of tremendous foreign influences unhindered by its formidable mountain ranges and vast deserts, is one of the most diverse parts of the world. It is the birthplace of two of the world’s great religions, the home of the largest cluster of human population, and is also the home of the world's greatest mountain ranges. The three largest countries of South Asian realm are India - the giant of the realm, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. The realm is highly diverse and populated. The diverse population has been brought together into political units that have roots in the realm’s colonial past. British colonialism had a significant impact on the realm. Many of the realm's contemporary political and cultural conflicts have roots in its colonial past.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Describe the realm’s physical geography. Identify each country’s main features and physical attributes and locate the realm’s main river systems.
- Describe the dynamics of the monsoon and how it affects human activities, and agricultural patterns in the region.
- Describe how European colonialism impacted the Indian Subcontinent.
- Describe the basic demographic trends the realm is experiencing. Describe how population growth is a primary concern of India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh.
- Describe how cultural, religious, and linguistic difference continue to cause conflict and division in countries of South Asia.
- Describe the historical roots of Kashmir conflict between India and Pakistan and the importance of Kashmir for both countries.
- Describe some contemporary environmental and socio-economic concerns of India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh
- Describe how Pakistan and Bangladesh were once under the same government, and what factors contributed to the separation of East Pakistan leading to the formation of Bangladesh.
- Describe East-West, north-South geographic differences in India.
- Describe the basic structure of caste system in Hindu religion.
To achieve the objectives listed above:
- Read the Module 9 Introduction
- Read Chapter #9 - South Asia in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 9 Assignment, Discussion posts, Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
Chapter 9: South Asia – World Regional Geography (pressbooks.pub)
-

Jakub Hałun, CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons
East Asia is a hub of ancient civilizations with proud cultural traditions and astonishing accomplishments, such as the dynasties of China which built the famous Great Wall. East Asia today contains a number of nations of global prominence and influence, including the People's Republic of China, Japan, and North and South Korea.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Outline the countries and territories that are included in East Asia. Describe the main physical features and climate types of each country (CLO 1, 3).
- Understand the relationship between physical geography and human populations in East Asia (CLO 1, 3, 4, 5).
- Describe how colonialism impacted China. Outline the various countries and regions that were controlled by colonial interests (CLO 1, 4).
- Summarize the main steps China has taken to transition from a strict Communist country established in 1949 to a more open society with a capitalist type of economy today (CLO 4, 6).
- Understand the population dynamics of China. Learn about the one-child-only policy and evaluate how it has affected Chinese society and culture (CLO 4, 6).
- Understand how North Korea and South Korea developed independently, and differ politically and economically today (CLO 4, 6).
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 10 Introduction
- Read Chapter #10 East Asia in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 10 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course outcomes 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6, and module learning objectives 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Then, you must respond to TWO of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are not required to post more than once, but feel free to respond to other posts and engage with your classmates
All three posts are due on Mondays by midnight, CST.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
Which of these three countries do you feel is most like the United States, and why: The People's Republic of China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Outline the countries and territories that are included in East Asia. Describe the main physical features and climate types of each country (CLO 1, 3).
-
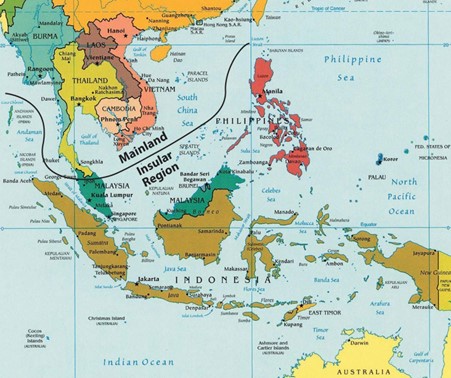
Southeast is the most fragmented realms of the world, both culturally and physically. The realm includes countries with political boundaries creating many shapes and sizes. The political borders were created through a combination of factors, including natural features, traditional tribal distinctions, colonial claims, and political agreements. The realm can be divided into two geographic regions: 1) The mainland portion, which is connected to India and China, extends south into what has been called the Indochina, a name given by France and suggesting the historical cultural influence of China and India; and 2) The insular region, which consists the islands of Southeast Asia occupied by the nations of Brunei, East Timor, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Singapore.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Describe the geographical differences between the mainland region and the insular region.
- Describe the historical cultural influence of China and India, and the cultural, economic, and political impact of European colonization on the realm.
- Describe the region's physiography, tectonic activity, and tropical climate.
- Describe the ethnic, cultural, religious, and linguistic diversity of the region.
- Describe the impact of physical geography of the region on its population dynamics.
- Describe the physical geography of Indonesia and the population dynamics of the island of Java.
- Describe the cultural characteristics of the Philippines and its importance for business process outsourcing (BPO).
To achieve the above listed objectives:
- Read the Module 11 Introduction
- Read Chapter #11 on Southeast Asia in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 11 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities.
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization Chapter 11
- Describe the geographical differences between the mainland region and the insular region.
-
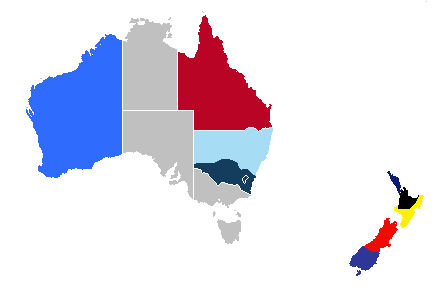
Map_of_Australia_and_New_Zealand.png: HatGregderivative work: Hatgreg (talk)derivative work: Craig t Moore, CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons
Australia and New Zealand have flora and fauna that are found nowhere else on Earth. Australia is distinctive because it is an island, a country, and a continent—the smallest of the world’s continents. No other land mass can concomitantly make those three claims. Australia consists of a large mainland and the island of Tasmania to the south. The main physical area of New Zealand, on the other hand, consists of two main islands separated from Australia’s southeastern region by the Tasman Sea.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Summarize how colonialism has affected the development and socioeconomic conditions of Australia and New Zealand. (CLO 4)
- Determine where the Wallace Line and the Weber Line were located. Understand how isolation has allowed for the high level of biodiversity. (CLO 1 & 3)
- Outline how colonialism impacted the Maori and the Aboriginal populations. (CLO 4)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 12 Introduction
- Read Chapter #12 - Australia and New Zealand in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 12 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item. -
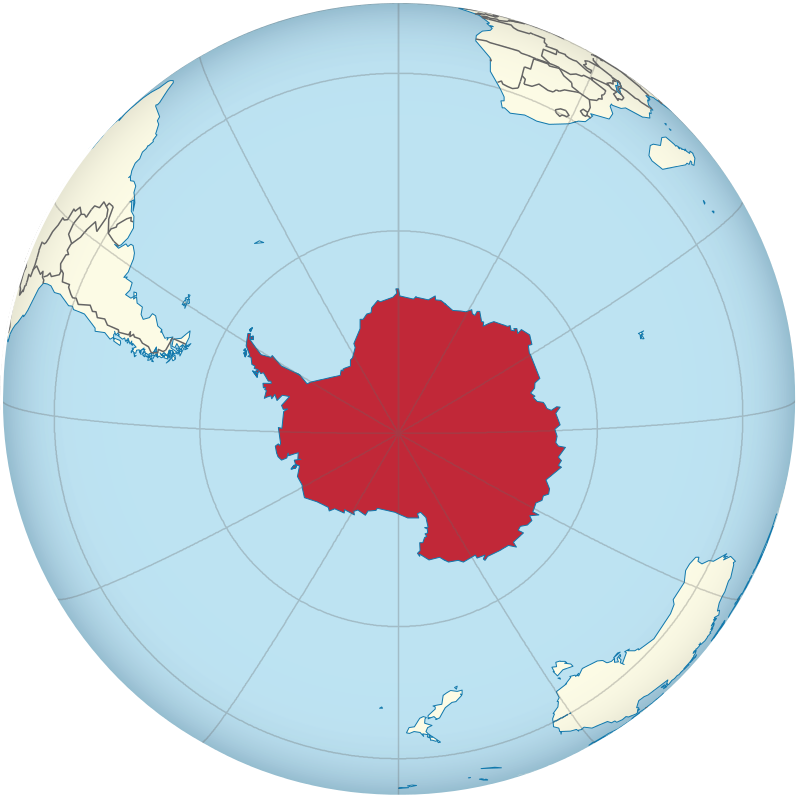
TUBS, CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons
The immense tropical Pacific realm and the ice-covered continent of Antarctica have almost opposing physical characteristics, but they are similar in that they are remote and isolated from the rest of the world. Understanding the geographic qualities of these two realms will help in comprehending the unique traits that humans have developed to survive in diverse environments. Both places include large physical areas with vast open spaces between human settlements. In the Pacific, human settlements are on islands. The only human settlements in Antarctica are isolated research stations. Historically, the South Pacific required a water-based transportation network, and in Antarctica, humans traveled across the snow and ice exploring the earth’s southern extremes.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Outline the three main areas of the South Pacific: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. (CLO 1)
- Distinguish between low islands and high islands. (CLO 3)
- Determine which islands remain under the auspices of France, the United Kingdom, New Zealand, or the United States. (CLO 4)
- Describe the primary economic activities of the islands in the realm. (CLO 4)
- Summarize the main environmental concerns of the islands in each region. (CLO 5)
- Read the Module 13 Introduction
- Read Chapter #13 - The Pacific and Antarctica in World Regional Geography: People, Places, and Globalization.
- Complete the Module 13 Assignment, Discussion Board Posts (3), Chapter Quiz, and H5P activities
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.World Regional Geography :People, Places and Globalization Chapter 13
-
-
Forum Instructions
In a post below, respond to the following prompt, which assesses course outcome (CLO 4), and module learning objective 4. Then, you must respond to TWO of your classmates' posts. After you post a response, you will be able to see other responses. You are not required to post more than once, but feel free to respond to other posts and engage with your classmates
All three posts are due on Mondays by midnight, CST.
Your response should be at least three to five sentences long. This includes responses to other students' posts. A simple “I agree” or “Yes” or “LOL” will not count. Please think about the questions and your peers' responses and reply thoughtfully and courteously, according to netiquette rules. Use good English grammar, correct punctuation, and complete sentences. While the posts will mostly be judged by their thoughtfulness and completeness, I reserve the right to take off points for grammatical errors, especially if they interfere with the clarity of the post.
Prompt
Describe the primary economic activities of the islands in the realm.
-
This assignment assesses course outcome (CLO 4), and module learning objective 3.
Write a 350-word essay in response to the following prompt. The essay must be submitted as a Microsoft Word (docx) file and must have 1-inch margins, use double spacing throughout with 12pt font. Proper grammar and spelling will be graded.
Discuss which islands remain under the auspices of France, the United Kingdom, New Zealand, or the United States.
